
Xin-Xiang Zhang
Peking University, China
Title: Glycan Profiling with new developed labelling reagent by LC-MS and sheathless interfaced CESI-MS/MS
Biography
Biography: Xin-Xiang Zhang
Abstract
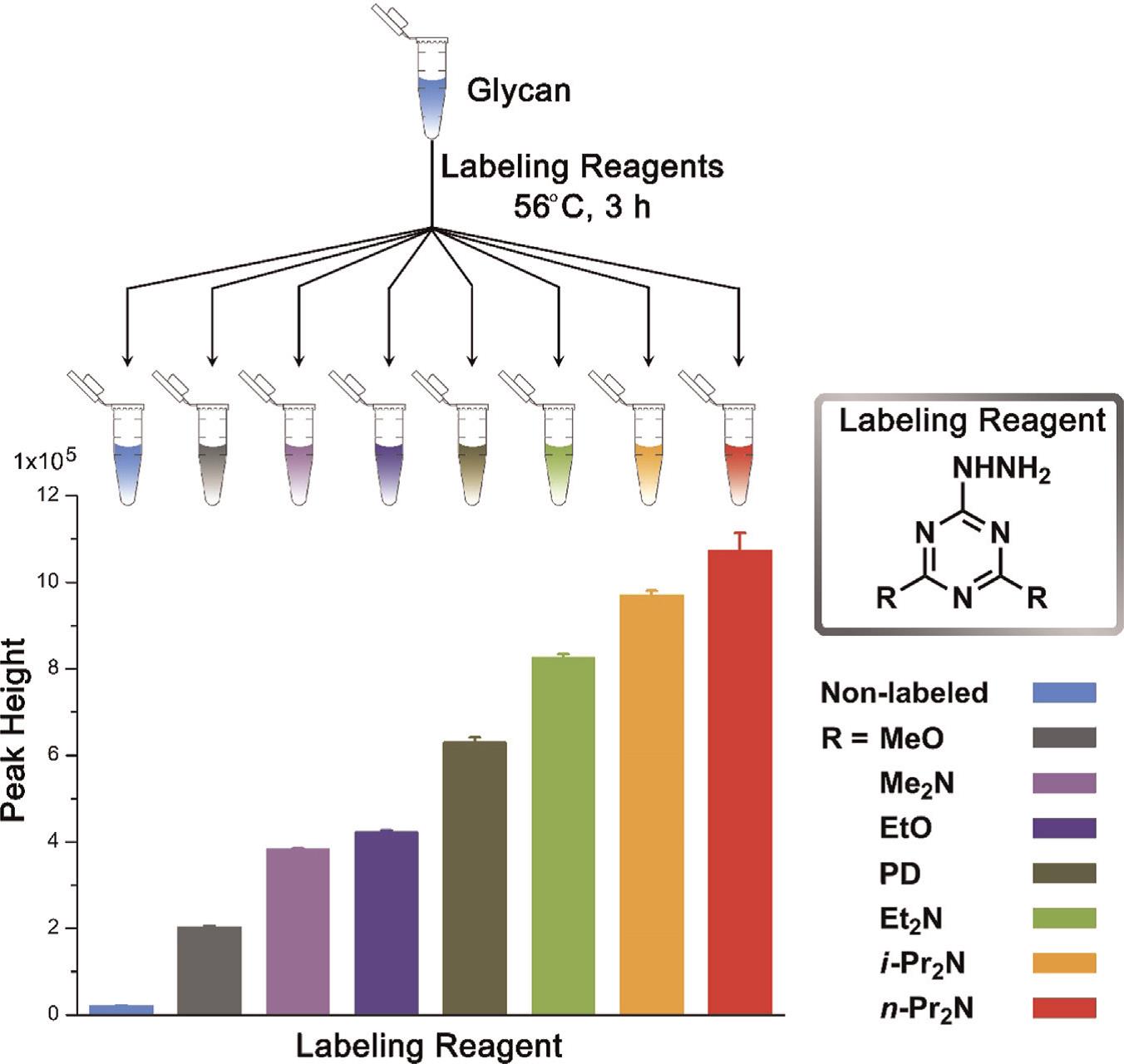
Labelling strategy plays an important role in mass spectrometry (MS) based glycan analysis due to the high hydrophilicity and low ionizationefficiency of glycans. We designed ten hydrazino-s-triazine based labelling reagents were synthesized under facile and controllable conditions for highly sensitive LC or CE–electrospray MS. Attached to N-glycans through non-reductive reactions, these new labelling reagents were evaluated in differently enhanced glycan response to MS. Three of them demonstrated to be reliable and remarkable for glycan analysis with satisfactory linearity and lowered limits of detection using maltoheptaose(DP7) as model. An innovative stable-isotope relative quantification strategy for N-glycans was achieved using these non-reductive hydrazino-s-triazine deuterated derivative as a labelling reagent combined with MS also. As much as a 20 Da mass shift could effectively distinguish different forms of Nglycans labelled with normal and heavy hydrazino-s-triazine at the reducing end. Especially for glycans with high molecular weight, qualitative identification could be significantly simplified on account of avoiding isotopic distributions overlapping in LC-MS or CE-MS. Furthermore, the most optimal labelling reagent was taken as an example for highly sensitive profiling of N-linked glycans both cleaved from chicken avidin and glyco- proteins in human serum, indicating prospective availability for these labelling reagents in frontier of glycomics researches. These reagents have been applied in the determination of trace amount of organic acids in environmental samples with highly sensitivity also.
Images

Recent Publications
- Zhang YW, Zhu J Yin H, Marrero J, Zhang X-X, Lubman D.M, (2015) ESI-LC-MS Method for Haptoglobin Fucosylation Analysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Liver Cirrhosis, J PROTEOME RESEARCH, 14 (12): 5388-5395
- Chen Z, Zhong X, Tie C, Chen BM, Zhang X-X, Li L, (2017) Development of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with MALDI-mass spectrometric imaging platformfor N-glycan relative quantitation using stable-isotope labeled hydrazide reagents, Anal and Bioanal Chem, in printing, DOI 10.1007/s00216-017-0387-6
- Zhao M-Z, Zhang YW, Yuan F, Deng Y, Liu JX, Zhou YL, Zhang X-X, (2015) Hydrazino-s-triazine based labelling reagents for highly sensitive glycan analysis via liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry , TALANTA 144:992-997
- Zhang YW, Zhao M-Z, Liu JX, Zhou YL, Zhang X-X, (2015) Double-layer poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated capillary for highly sensitive and stable capillary electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis with mass spectrometry glycan analysis, J. Sep Sci, 38:475-482
- Zhao M-Z, Tie C, Zhang YW, Deng Y, Zhang FT, Zhou YL, Zhang X-X, (2015) Deuterated hydrazino-s-triazine as highly-efficient labelling reagent for glycan relative quantification analysis using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, RSC ADVANCES 5:79317-79322
- Liu JX, Zhang YW, Yuan F, Chen H-X, Zhou YL, Zhang X-X, (2014) Differential detection of Rhizoma coptidis by capillary electrophoresis electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with a nanospray interface ELECTROPHORESIS, 35:21-22
- Tie C, Hu T, Zhang X-X, Zhou J, Zhang J-L, (2014) HPLC-MRM relative quantification analysis of fatty acids based on a novel derivatization strategy ANALYST, 19:6154-6159
- Zhang YW, Li Z, Zhao Q, Zhou YL, Liu HW, Zhang X-X(2014) A facilely synthesized amino-functionalized metal-organic framework for highly specific and efficient enrichment of glycopeptides CHEMICAL COMMUNICATIONS 50:10504-10506
- Liu JX, Zhao MZ, Deng Y, Tie C, Chen H-X, Zhou YL, Zhang X-X, (2014) The coating of smart pH-responsive polyelectrolyte brushes in capillary and its application in CE ELECTROPHORESIS 34:1352-1358
- Tie C, Zhang X-X, A new labelling reagent for glycans analysis by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry ANALYTICAL METHODS 4:357-359

