
Andrzej Kubaczka
Opole University, Poland
Title: Predicting mass fluxes in the pervaporation process of alcohols dehydration using Maxwell-Stefan diffusion coefficients
Biography
Biography: Andrzej Kubaczka
Abstract
Pervaporation is the process that actually in the world industry is applied in majority to dehydration of organic solvents. Most generally, the mass fluxes in the pervaporation process are a function of all mass transport resistances occurring in the mass transport path. The membrane is the heart of pervaporation process and from its permeation properties depends the yield and selectivity of the process. Depending on the construction of pervaporation unit, some other mass transfer resistances can be neglected. The majority of the methods of calculation the mass fluxes in the polymer membranes based on the generalized Fick's equation, while for calculation of mass fluxes in fluid systems the generalized Maxwell-Stefan equations (GMSE) is preferably used. Recently Kubaczka proposed the method that allows prediction Maxwell-Stefan diffusion coefficients (MSD) in the membrane space for multicomponent systems using self-diffusion coefficients and binary diffusion coefficients for infinitely diluted mixtures. The purpose of this study is the test of an accuracy of the prediction of mass fluxes in the pervaporation process based on GMSE where MSD are predicted according to the proposed method. These calculations have been done for the experimental results of pervaporation of the isopropanol-water and ethanol-water mixtures in the poly (vinyl alcohol) membrane. These data were the results of the experiments conducting on the PERVAP 2210 hydrophilic membrane. The self-diffusion coefficients, which are the most important element of analyzed method, were predicted using formulas derived from the free-volume theory by Vrentas and Vrentas . The equilibrium concentrations on both sides of the separating polymer film were computed using UNIFAC-FV method with FV element modified according to the model of Kannan et al. The comparison of calculated and experimental results shows very good agreement between experimental and predicted data. The influences of free volume parameters on the mass fluxes are also analyzed.
Image
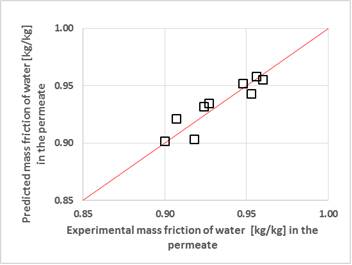
Figure 1: Comparison of the predicted and experimental mass frictions of water [Kg/Kg] in the permeate
Publications
- Lipnizki F. and Trägårdh G. (2001) Modelling of pervaporation: Models to analyze and predict the mass transport in pervaporation. Separation and Purification Methods 30(1):49-125.
- Shao P., Huang R.Y.M. (2007) Polymeric membrane pervaporation. Journal of Membrane Science 287: 162-179.
- Kubaczka A. (2014) Prediction of Maxwell–Stefan diffusion coefficients in polymer - multicomponent fluid systems, Journal of Membrane Science 470: 389-398.
- Vrentas J.S., Vrentas Ch.M. (1998) Predictive Methods for Self-Diffusion and Mutual Diffusion Coefficients in Polymer-Solvent Systems, Eur. Polym. J. 34:797-803.
- Kannan D.C., Duda J.L., Danner R.P. (2005) A free-volume term based on the van der Waals partition function for the UNIFAC model. Fluid Phase Equilibria. 228-229: 321-328.

