
Mahmoud A. Abdulhamid
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Saudi Arabia
Title: Synthesis and gas transport properties of substituted bicyclodianhydride-based polyimides
Biography
Biography: Mahmoud A. Abdulhamid
Abstract
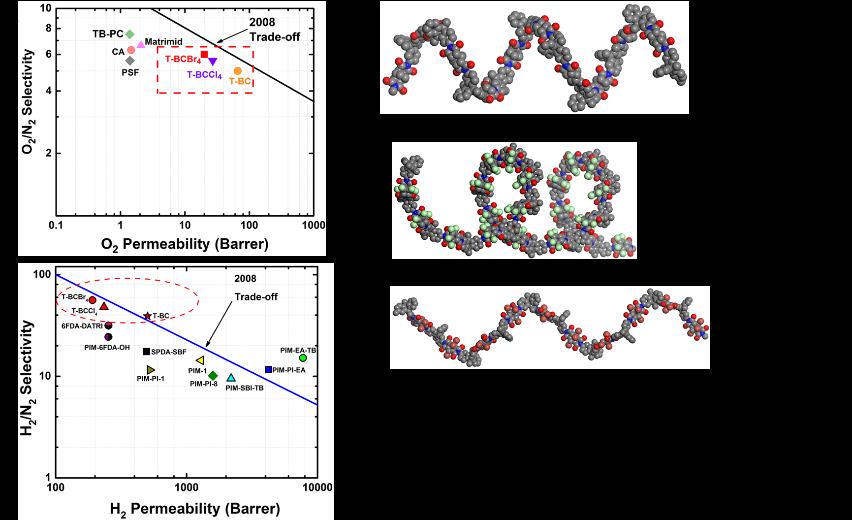
Three novel polyimides were synthesized from a 9,10-dimethyl-2,6(7)-diaminotriptycene (T) with a commercially available bicyclo[2.2.2]oct-7-ene-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BC) and its halogenated derivatives. The non-halogenated T-BC polyimide derivative was made as a reference material to evaluate the effect of the halogen groups in T-BCCl4 and T-BCBr4 on its gas transport properties. Pure-gas permeability coefficients of He, H2, N2, O2, CH4, and CO2 were measured at 35 °C and 2 atm. The BET surface area based on nitrogen adsorption at 77 K of T-BC was 570 m2 g-1 while those of tetrachloro-functionalized T-BCCl4 and tetrabromo-functionalized polyimide T-BCBr4 were reduced significantly to 340 and 30 m2 g-1, respectively. The decrease in BET surface area in the halogenated polyimides resulted from reduction in their pore volumes relative to that of T-BC due to occupation of free volume space by the halogens. The freshly prepared T-BC membrane had a pure-gas O2 permeability of 66 Barrer and O2/N2 selectivity of five. The permeability decreased significantly by replacing the hydrogen groups by the chloro- or bromo groups in the cycloaliphatic dianhydride building block. For example, the permeability of O2 decreased by 3-fold from 66 in T-BC to 20 Barrer in T-BCBr4, while the permeability of nitrogen was reduced from 13 to 3.4 Barrer. As expected for lower permeability polymers, the O2/N2 selectivity increased concurrently from 5 in T-BC to 6 in T-BCBr4. Long-term testing over 365 days resulted in only ~ 15% loss in gas permeability’s and without significant changes in selectivity’s, which demonstrated that these polyimides were resistant to physical aging. These combined results suggest that BC-based polyimides are promising candidate membrane materials for gas separation applications.
Image
Publications
- Matsumoto, T. and T. Kurosaki, Soluble and Colorless Polyimides from Bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic 2,3:5,6-Dianhydrides. Macromolecules, 1997. 30(4): p. 993-1000.
- Chun, B.-w., Preparation and characterization of organic-soluble optically transparent polyimides from alicyclic dianhydride, bicyclo[2.2.2]-oct-7-ene-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic dianhydride. Polymer, 1994. 35(19): p. 4203-4208.
- Liu, J.G., et al., Organosoluble and transparent polyimides derived from alicyclic dianhydride and aromatic diamines. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2002. 40(1): p. 110-119.
- Ma, X., et al., Novel Spirobifluorene- and Dibromospirobifluorene-Based Polyimides of Intrinsic Microporosity for Gas Separation Applications. Macromolecules, 2013. 46(24): p. 9618-9624.
- Pascoe, E.V. and I.I. Harruna, Synthesis and characterization of high temperature polyimides from bicyclic dianhydrides. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A, 2003. 40(9): p. 915-932.

